The Ayodhya Ram Mandir is a sacred Hindu temple located in Ayodhya, a city in the north Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. The temple is said to be the birthplace of Lord Ram, one of the most revered deities in Hinduism. The Ayodhya Ram Mandir has been at the center of a contentious dispute for many years, making it one of the most controversial religious sites in India.
Key Takeaways:
- Ayodhya Ram Mandir is a holy Hindu temple located in Ayodhya, Uttar Pradesh.
- The temple is believed to be the birthplace of Lord Ram, a highly revered deity in Hinduism.
- The Ayodhya Ram Mandir is the center of a long-standing controversy.
- The temple’s construction and architectural design are still ongoing.
- The Ayodhya Ram Mandir holds significant spiritual and religious importance for Hindus worldwide.
The Ancient City of Ayodhya
Ayodhya is an ancient city located in the north Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is situated on the banks of the Sarayu River and is considered one of the seven most sacred places in Hinduism. The city has a rich cultural and spiritual heritage and is believed to be the birthplace of Lord Ram, the seventh avatar of Lord Vishnu.
Ayodhya’s history goes back thousands of years, with archaeological evidence indicating that it was inhabited as early as the 9th century BCE. Over the centuries, the city has been ruled by numerous powerful dynasties, including the Mauryans, Guptas, and Mughals. Ayodhya is home to several significant religious sites, including the Hanuman Garhi temple, the Kanak Bhawan temple, and the Nageshwarnath temple. The city is also known for its vibrant ghats, where devotees gather to offer prayers and perform rituals.
“The glory of Ayodhya was such that it could never be destroyed, and the memories of this ancient city would always remain etched in our hearts and minds.” – Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru
The Ayodhya Kanda
The ancient city of Ayodhya is also famous for its association with the Ayodhya Kanda, a section of the Hindu epic Ramayana. The Ayodhya Kanda describes the story of Lord Ram’s birth and his early years growing up in the city. The epic also details the events that led to Lord Ram’s exile from Ayodhya and his eventual triumph over the demon king Ravana.
Ayodhya | Height Above Sea Level (m) | Population |
Ayodhya | 93 | 77,000 |
Ayodhya’s ancient temples and monuments attract millions of pilgrims and tourists from around the world each year. Visitors can explore the city’s rich history, take part in religious ceremonies and festivals, and enjoy traditional Indian cuisine at the many local restaurants and street food vendors.
The ancient city of Ayodhya is a fascinating destination that offers an incredible glimpse into India’s rich cultural and spiritual heritage. Whether you’re a history buff, a religious pilgrim, or simply a curious traveler, Ayodhya is a must-visit destination that is sure to leave a lasting impression on your heart and soul.
The Legend of Lord Ram
Lord Ram, one of the most revered deities in Hinduism, was believed to be the seventh incarnation of Lord Vishnu, the preserver of the universe. According to ancient Indian texts such as the Ramayana and the Mahabharata, Ram was born in Ayodhya to Queen Kaushalya and King Dasharatha during the Treta Yuga, a time period over two million years ago.
As a prince, Ram was adored by all for his intellect, compassion, kindness, and dedication to righteousness. However, he was exiled from his kingdom by his own father for 14 years, after which he embarked on a perilous journey, accompanied by his wife Sita and his brother Lakshman.
During his exile, he encountered numerous challenges, including a battle with the demon king Ravana, who had abducted Sita. Ram, with the help of Hanuman and an army of monkeys, rescued Sita and returned to Ayodhya to reclaim his rightful place as king.
The story of Ram’s journey has been passed down for generations and remains an integral part of Hindu mythology and culture. His virtuous character and unwavering devotion to righteousness continue to inspire people to this day.
The Controversy Surrounding Ayodhya Ram Mandir
The construction of the Ayodhya Ram Mandir has been mired in controversy for decades. The dispute over the site has been a long-standing issue between Hindus and Muslims, with each community claiming ownership.
The controversy dates back to the 16th century when the Babri Masjid was built on the site. Hindus claim that it was built after destroying a Ram Mandir that existed at the same spot, while Muslims contend otherwise, stating that the Masjid was built on an empty plot of land.
Several attempts have been made by both communities to claim the site over the years, leading to communal tensions and violence. The issue has also been dragged through the legal system for years, with both sides presenting their cases to the courts.
However, the issue came to a head in 1992 when the Babri Masjid was demolished by a mob of Hindu extremists, leading to riots across the country. The demolition sparked outrage among the Muslim community, and the issue has remained a divisive topic since then.
Finally, in 2019, the Indian Supreme Court settled the dispute by awarding the site to Hindus and directing the government to allocate an alternative plot of land for the construction of the Masjid. The verdict was met with mixed reactions from both communities, with some welcoming it and others condemning it.
Historical Background of Ayodhya Ram Mandir
The Ayodhya Ram Mandir, also known as the Ram Janmabhoomi, is a revered Hindu pilgrimage site located in Ayodhya, Uttar Pradesh, India. The history of this sacred site dates back to the 16th century during the Mughal era.
The first historical evidence of a temple at the site of the Ayodhya Ram Mandir can be traced back to the 11th century when the temple was constructed by King Raja Suheldev. However, the present temple that stands at the site is believed to be built over the ruins of the ancient temple during the 16th century under the patronage of Mughal Emperor Babur.
Over time, the Ayodhya Ram Mandir and its surroundings became sacred spaces for the Hindu community and an essential pilgrimage site for devotees. In the 19th century, the British colonial government established a separate administration for the Ayodhya Ram Mandir, reflecting its growing religious significance.
The temple underwent several structural changes and renovations under different rulers, including the Maratha ruler Jiwan Rao Scindia, Ahilyabai Holkar of Indore, and Rani Ahilya Bai of Gwalior. The temple’s architectural grandeur is a unique blend of different styles, including Rajput, Mughal, and South Indian Dravidian architecture.
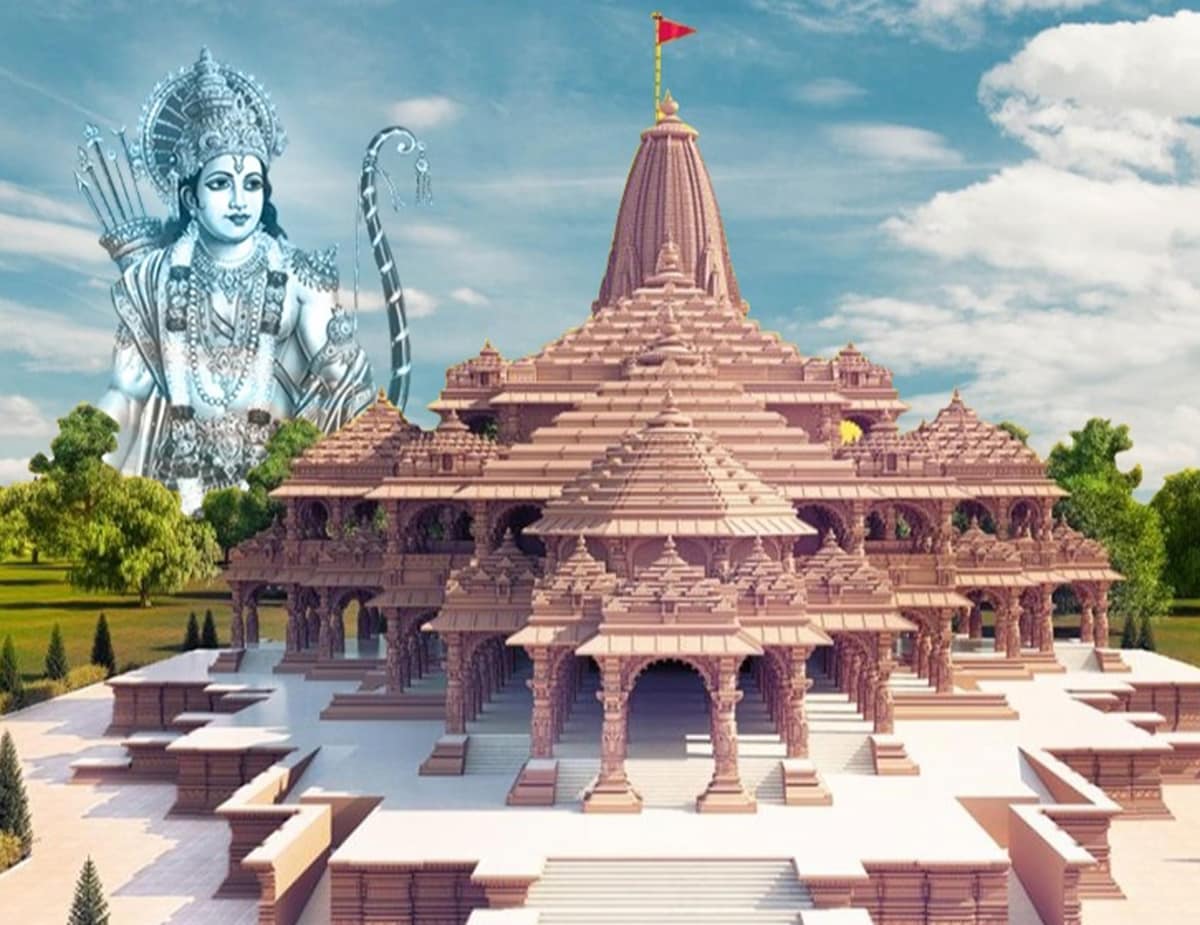
The Architecture of Ayodhya Ram Mandir
The Ayodhya Ram Mandir, built over the ruins of the ancient temple, is a unique combination of different architectural styles, reflecting the diverse cultural influences in India. The temple features three domes, resembling the shape of a conch shell, a Hindu symbol of purity and auspiciousness.
The temple’s three floors stand on 106 pillars, each carved with figures of apsaras (celestial dancers), animals, flowers, and warriors. The temple’s sanctum sanctorum houses the idol of Lord Ram, along with other deities such as Sita, Lakshman, and Hanuman.
Features of Ayodhya Ram Mandir | Architecture Styles |
Three domes | Mughal |
106 pillars | Rajput |
Ancient carvings | Dravidian |
The temple’s exterior is decorated with intricate carvings and sculptures of Hindu deities, including Garuda, Nandi, and elephants. The temple’s walls also feature verses from the Ramayana, illustrating Lord Ram’s life and his journey.
Despite many controversies, the Ayodhya Ram Mandir has remained a symbol of faith, spirituality, and cultural heritage for millions of Hindus around the world.
Ayodhya Ram Janmabhoomi
Ayodhya Ram Janmabhoomi is a significant place of worship for Hindus, believed to be the birthplace of Lord Ram. The word Janmabhoomi translates to “birthplace”, hence reflecting the importance of the location for the Hindu community.
The city of Ayodhya is considered a holy site, where ancient scriptures describe the presence of the revered Lord Ram. As per Hindu mythology, Lord Ram appeared in Ayodhya thousands of years ago, in a time when evil was rampant, and people lived in fear.
“Ram Janmabhoomi is more than just a religious site, it is our faith and belief. Its construction is a monumental event for the entire Hindu community, and an embodiment of our deeply cherished aspirations.”
– Ram Nath Kovind, Former President of India
The Ayodhya Ram Janmabhoomi dispute over the construction of the Ram Mandir has been a longstanding issue. However, it finally culminated with the landmark verdict of the Supreme Court in November 2019, granting permission to build the Ram Mandir at the site.
After years of legal battles and social unrest, the construction of the grand Ram Mandir is underway, and it is expected to be a marvel of architecture and spiritual significance once completed.
The Babri Masjid Demolition
The Babri Masjid was a mosque built in Ayodhya during the Mughal period, but in 1992, it became the center of a political conflict between Hindus and Muslims that ultimately led to its demolition. The demolition was a controversial event that sparked communal riots in different parts of India and left behind lasting social and political scars.
The conflict stemmed from a belief held by Hindus that the mosque was built on the birthplace of Lord Ram, a revered deity. This belief heightened tensions and led to a protracted legal battle in the Indian courts, which finally culminated in a Supreme Court verdict that allowed the construction of a Ram temple in Ayodhya.
The demolition of the Babri Masjid was a major flashpoint in the Ayodhya Ram Mandir dispute that had been simmering for years. The incident marked a turning point in Indian politics, with many political analysts attributing the rise of Hindu nationalism to the events that unfolded in Ayodhya that day.
“The demolition of the Babri Masjid was a black day in the history of Indian democracy. The fact that the mosque was brought down despite heavy security is a testimony to the failure of the state machinery to prevent the escalation of violent tensions.”
Although the incident itself is now in the past, its legacy continues to shape the political and social landscape of India. For many Muslims, the Babri Masjid demolition remains a symbol of religious discrimination, an event that highlights the deep-seated prejudices and inequalities that continue to plague Indian society.
Legal Battle and Supreme Court Verdict

The legal battle surrounding the Ayodhya Ram Mandir controversy was one of the most contentious issues in India. The dispute centered on whether the land on which the Babri Masjid mosque was built belonged to Hindus or Muslims. The issue had been simmering for decades, and tensions came to a head when the mosque was demolished in 1992 by Hindu extremists, sparking widespread violence and communal riots across the country.
The legal proceedings began shortly after the demolition of the mosque, with both sides filing multiple suits claiming ownership of the disputed land. For almost three decades, the case remained intensely controversial with supporters of both sides arguing their claims energetically.
On November 9, 2019, the Supreme Court of India delivered its verdict, ending the decades-long dispute once and for all. The court ruled that the disputed site would be handed over to a trust to build a Ram temple, while Muslims were to be given land elsewhere to construct a mosque. The court’s landmark verdict was seen as a historic moment in Indian history, ending one of the country’s most divisive legal battles.
The judges ruled that Hindus had a spiritual connection to the land where the mosque stood, and that there was enough historical evidence to support their claim that the temple had stood there earlier. Muslims, who had been worshipping at the mosque for centuries before it was destroyed, were to be given five acres of land nearby to build a new mosque, thus ending the religious rift.
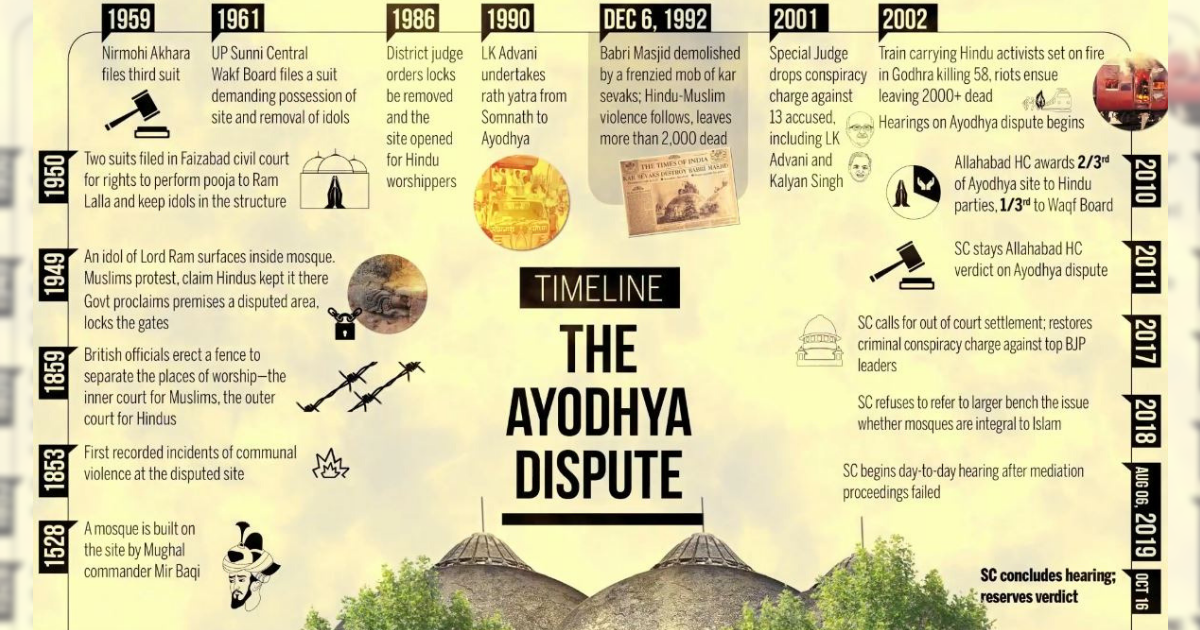
Timeline of Ayodhya Legal Battle
Year | Event |
1853 | Babri Masjid mosque built by Mughal emperor Babur |
1885 | Mahant Raghubir Das files the first court case seeking permission to build a Ram temple |
1949 | Lord Ram idols placed inside the mosque |
1986 | Local court orders removal of the idols and locks the gates of the mosque |
1990 | Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) launches the Ram Janmabhoomi movement, leading to widespread protests and Hindu-Muslim riots |
1992 | Hindu extremists demolish the Babri Masjid mosque, leading to nationwide riots |
1993 | CBI takes over the case, files conspiracy charges against top BJP leaders and members of VHP |
2002 | 59 people, mostly Hindus, die in a train fire in Godhra, Gujarat. Hindu mob retaliates with the massacre of over 2,000 Muslims |
2010 | Allahabad High Court rules that the disputed land be divided into three parts, with two-thirds to be given to Hindus and one-third to Muslims |
2011 | Supreme Court stays the Allahabad High Court verdict |
2019 | Supreme Court delivers a historic verdict, handing over the disputed land to build the Ram temple and allocating five acres of land to the Muslim community to construct a new mosque |
The legal battle and Supreme Court verdict have brought an end to the Ayodhya Ram Mandir controversy that had plagued India for almost three decades. Today, the construction of a magnificent Ram temple in Ayodhya is underway, marking a significant turning point in the cultural and spiritual journey of India.
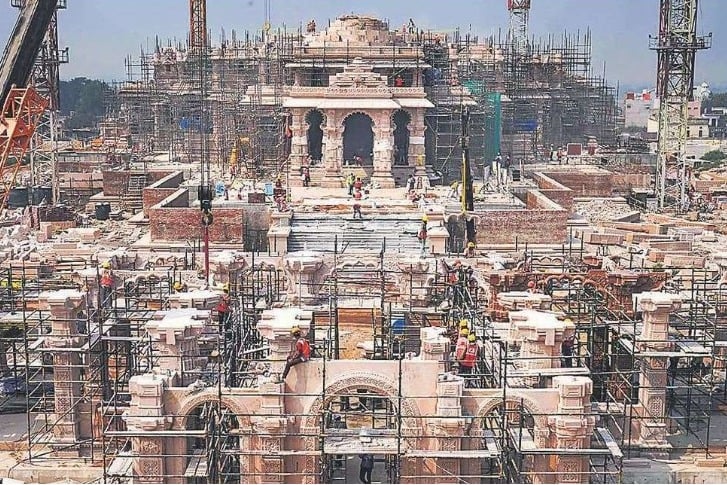
Ram Mandir Construction and Architecture
The construction of the Ram Mandir is a significant event in the history of India and one that has finally come to fruition after decades of controversy and legal battles. The Mandir is being built in the heart of Ayodhya city in the state of Uttar Pradesh and is expected to be completed in the near future.
The architecture of the new temple is unique and draws inspiration from the ancient Nagara style of architecture. The temple will feature a grand central dome, multiple small shikharas, and intricate stone carvings depicting the Ramayana and other Hindu mythologies. The use of sandstone from Rajasthan in the construction of the temple adds to its majestic aura.
The temple complex will also house other structures, including a museum, a library, and a research center that will provide valuable insights into the history and culture of the city. The complex is being built according to Vastu Shastra, an ancient Indian architectural science that ensures the harmony and balance of elements in a structure.
Key Features | Details |
Dimensions | The temple will have a length of 360 feet, width of 235 feet, and a height of 161 feet. |
Main Dome | The central dome is 162 feet high and has a diameter of 96 feet. |
Shikharas | The temple will have five other shikharas, each measuring around 140 feet in height. |
Construction Material | The temple will be constructed using sandstone from Rajasthan. |
Architectural Style | The temple will have an architecture inspired by the ancient Nagara style of architecture. |
The Ram Mandir is not just a place of worship but has emerged as an architectural masterpiece and a symbol of India’s rich cultural heritage. Its completion will mark a historic achievement and will pave the way for greater religious harmony and unity in the country.
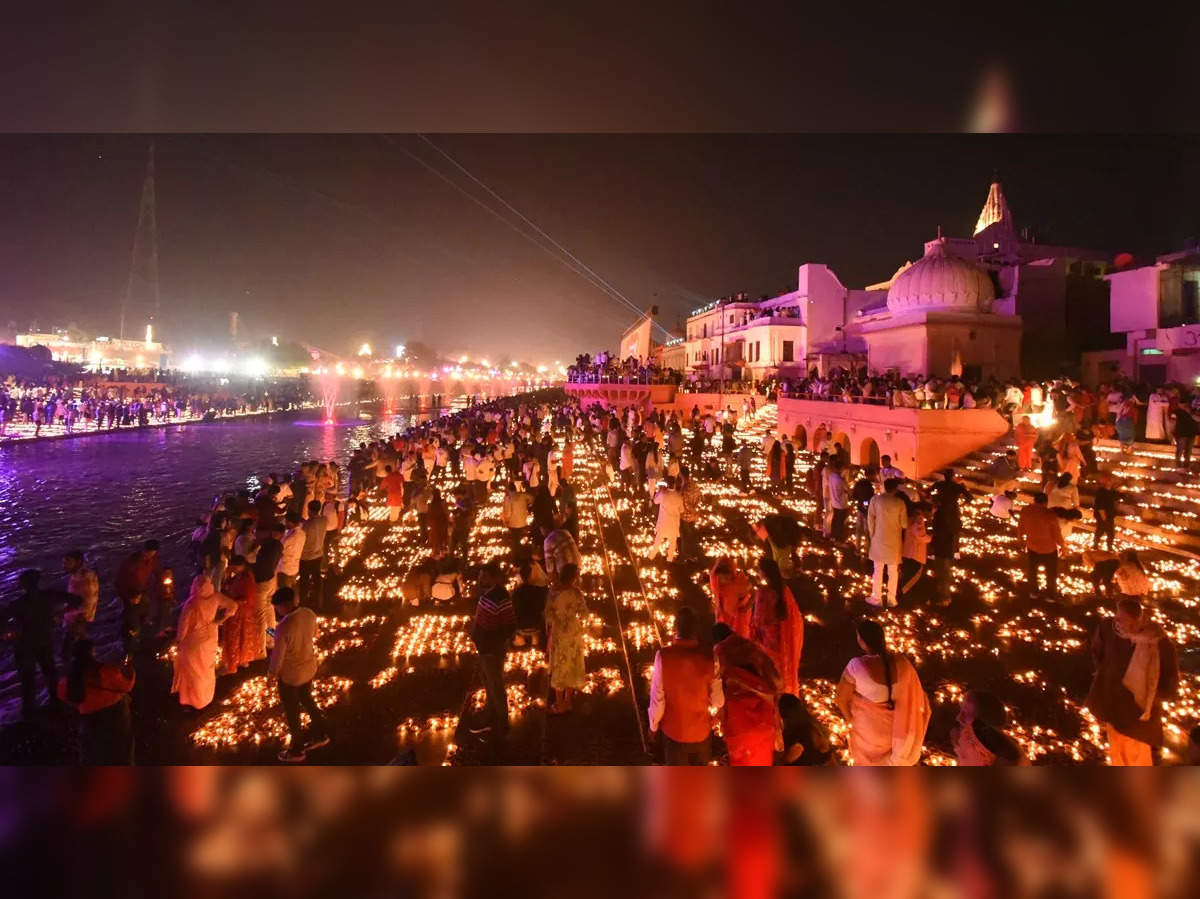
Pilgrimage and Spiritual Significance
The Ayodhya Ram Mandir is a revered holy site, drawing millions of pilgrims from across the world every year. As the birthplace of Lord Ram, it holds immense spiritual significance in Hinduism, with devotees undertaking the pilgrimage to seek blessings and salvation.
According to Hindu mythology, Lord Ram is believed to embody the qualities of truth, righteousness, and compassion, making him a popular figure amongst devotees. The journey to Ayodhya Ram Mandir is considered a sacred experience, with many devotees undertaking the arduous trek to seek blessings from Lord Ram.
Pilgrimage Highlights | Spiritual Significance |
Visiting the Ram Janmabhoomi site, considered the birthplace of Lord Ram | Seeking the blessings of Lord Ram for good health, prosperity, and success |
Performing aarti and puja at the Ayodhya Ram Mandir for cleansing and purification | Attaining moksha, liberation from the cycle of birth and rebirth |
Participating in the Ram Navami festival, celebrated with great fervor in Ayodhya | Experiencing spiritual growth and enlightenment |
The Ayodhya Ram Mandir is not only a site of pilgrimage but also a symbol of India’s rich cultural heritage and religious diversity. As the construction of the magnificent Ram Mandir nears completion, it represents a significant milestone in the resolution of a long-standing controversy and the restoration of peace and harmony in the region.
For devotees, visiting the Ayodhya Ram Mandir is a life-changing experience, inspiring them to lead a life of righteousness, truth, and compassion. Its spiritual significance and timeless legacy will continue to inspire generations to come.
Conclusion
The Ayodhya Ram Mandir stands as a symbol of India’s rich cultural and spiritual heritage. From its ancient origins to the legal battle, controversies, and ultimate triumph, the Ayodhya Ram Mandir represents not just a physical structure, but also a testament to the resilience of the Indian people and their faith.
The construction of the magnificent Ram Mandir marks the fulfillment of a long-standing dream and the start of a new chapter in the rich history of Ayodhya. As a sacred pilgrimage site, the Ayodhya Ram Mandir remains a beacon of hope, inspiration, and faith for millions of people around the world.
The Ayodhya Ram Mandir represents not just a place of worship, but also a powerful symbol of India’s unity in diversity, promoting peace, harmony, and mutual respect. With its grand architecture and rich history, the Ayodhya Ram Mandir is sure to continue to captivate and inspire generations to come.
FAQ
What is the history and significance of the Ayodhya Ram Mandir?
The Ayodhya Ram Mandir has a rich history and holds immense spiritual significance. It is believed to be the birthplace of Lord Ram, a revered figure in Hinduism. The temple stands as a symbol of devotion and faith for millions of devotees.
Can you tell me about the ancient city of Ayodhya?
Ayodhya is an ancient city known for its religious and cultural heritage. It is considered one of the seven sacred cities in Hinduism and is closely associated with Lord Ram. The city attracts pilgrims from all over the world who come to visit the Ayodhya Ram Mandir and other holy sites.
What is the legend surrounding Lord Ram?
Lord Ram is a prominent figure in Hindu mythology. He is believed to be the seventh avatar (incarnation) of Lord Vishnu. The legend of Lord Ram revolves around his birth, his victory over the demon king Ravana, and his teachings on righteousness and devotion.
What is the controversy surrounding the Ayodhya Ram Mandir?
The controversy surrounding the Ayodhya Ram Mandir revolves around the claim for the land on which the mosque known as the Babri Masjid stood. The dispute pertains to whether the mosque was constructed on the site where Lord Ram was believed to have been born. The issue has been a subject of legal battles and social tension for many years.
What is the historical background of the Ayodhya Ram Mandir?
The Ayodhya Ram Mandir has a long and fascinating historical background. Its construction dates back centuries, with different rulers and empires contributing to its architectural evolution. The temple represents a blend of various architectural styles and holds significance as a place of worship for Hindus.
What is the significance of Ayodhya Ram Janmabhoomi?
Ayodhya Ram Janmabhoomi is believed to be the exact birthplace of Lord Ram. It holds great importance to devotees who consider it a sacred site worthy of reverence and worship. The construction of the Ram Mandir at Ayodhya Ram Janmabhoomi is seen as a fulfillment of a longstanding aspiration for Hindus.
Can you explain the Babri Masjid demolition and its impact on the Ayodhya Ram Mandir dispute?
The Babri Masjid was a mosque built in Ayodhya during the 16th century. It stood on a site claimed by Hindus to be the birthplace of Lord Ram. In 1992, the mosque was demolished by a group of individuals, leading to widespread communal tension and a protracted legal battle over the land’s ownership.
What was the legal battle surrounding the Ayodhya Ram Mandir, and what was the Supreme Court verdict?
The legal battle over the Ayodhya Ram Mandir involved multiple parties representing different religious and communal interests. The Supreme Court of India, in its landmark verdict in November 2019, granted permission for the construction of the Ram Mandir at the disputed site, while also allotting an alternate plot for the construction of a mosque.
Can you provide information about the construction and architecture of the Ram Mandir?
The ongoing construction of the Ram Mandir aims to create a magnificent temple that reflects the architectural grandeur and devotion associated with Lord Ram. The design draws inspiration from traditional Hindu temple architecture, incorporating intricate carvings, sculptures, and symbolic elements that resonate with Hindu beliefs and mythology.
What is the significance of the Ayodhya Ram Mandir as a pilgrimage site and its spiritual importance in Hinduism?
The Ayodhya Ram Mandir holds immense significance as a pilgrimage site for Hindus. Devotees from all over the world visit the temple to seek blessings and offer their prayers to Lord Ram. The site is considered a spiritually potent place, believed to bestow divine grace and fulfill devotees’ desires.